On November 19, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals announced that the European Commission (EC) has granted marketing authorization for the RNAi therapeutic Oxlumo (lumasiran) for the treatment of primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (PH1) in all age groups. This approval makes lumasiran the third RNAi therapy approved by the company in the past three years.
PH1 is a rare disease in which the overproduction of oxalate leads to the deposition of calcium oxalate crystals in the kidneys and urinary tract, and may lead to pain and recurrent kidney stone formation and renal calcification. Impaired kidney function can aggravate the disease, because excessive oxalate will not be effectively excreted, leading to subsequent accumulation and crystallization of bones, eyes, skin, and heart, leading to serious illness and death. Although a small number of patients respond to vitamin B6 therapy, there is currently no approved treatment for PH1.
Lumasiran is the first potential therapy to show a significant reduction in urine oxalate excretion. The results from the Phase III ILLUMINATE-A study (NCT03681184) show that lumasiran significantly reduces the production of oxalate in the liver, which may solve the inherent pathophysiological problem of PH1. If approved for marketing, lumasiran will have a meaningful clinical impact on PH1 patients.
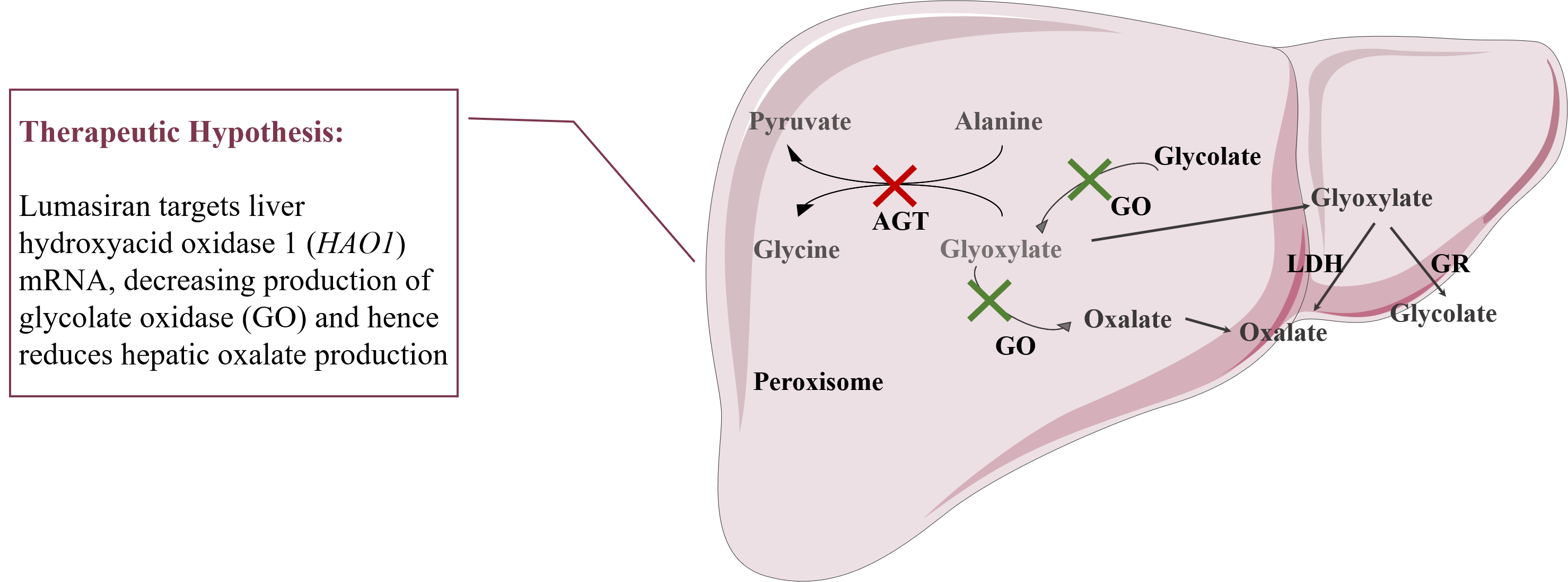 Figure 1: Therapeutic hypothesis of lumasiran.
Figure 1: Therapeutic hypothesis of lumasiran.
Lumasiran is a subcutaneously administered RNAi therapeutic drug targeting hydroxy acid oxidase 1 (HAO1), developed for the treatment of primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (PH1). HAO1 encodes glycolate oxidase (GO), which is upstream of the disease-causing defect in PH1. Lumasiran works by degrading HAO1 messenger RNA and reducing the synthesis of GO. The synthesis of GO inhibits the production of oxalate in the liver, which is a toxic metabolite responsible for the clinical manifestations of PH1. In the key ILLUMINATE-A study, lumasiran was shown to significantly reduce oxaluria levels compared to placebo, and most patients reached normal or close to normal levels.
Lumasiran adopts the latest enhanced and stable chemical ESC-GalNAc conjugate technology developed, which can make subcutaneous administration have stronger efficacy and durability, and has a broad therapeutic index.
RNAi (RNA interference) is the natural cellular process of gene silencing and represents one of the most promising and rapidly developing fields in biology and drug development today. Its discovery is hailed as "a major scientific breakthrough that occurs every ten years or so" and won the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. By taking advantage of the natural biological process of RNAi in our cells, a new kind of drug called RNAi therapeutic has now become a reality.
Related Articles
RNAi uses small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules to bind complementary messenger RNA, triggering its degradation and preventing the production of specific proteins in cells.
Key considerations include target mRNA accessibility, sequence specificity, off-target minimization, and thermodynamic stability to ensure efficient gene knockdown.
RNAi can selectively downregulate genes involved in metabolic pathways, enabling researchers to study enzyme function, protein regulation, or control of metabolite production in various systems.
Chemical modifications like GalNAc conjugates enhance siRNA stability, cellular uptake, and target tissue specificity, improving experimental reproducibility and gene silencing efficiency.
Custom services provide design, synthesis, quality control, and delivery optimization, reducing experimental time and supporting targeted studies in gene function and pathway modulation.
Yes, RNAi allows precise gene knockdown in cellular or tissue models, offering insights into disease mechanisms, metabolic regulation, and potential intervention points for research purposes.