BOC Sciences' custom LNA synthesis service is a high quality, accurate LNA (Locked Nucleic Acid) synthesis service. Our LNA synthesis service provides fast, reliable, and efficient solutions to meet the unique needs of our customers. Our dedicated team uses the latest synthesis technologies and advanced equipment to ensure that we provide our customers with the highest quality LNA products.
Locked nucleic acid (LNA) is a modified RNA nucleoside analog consisting of one or more LNA nucleotide monomers in which the bicyclic furanose unit is locked in an RNA mimetic sugar conformation. LNA oligonucleotides have good recognition and strong affinity for DNA and RNA. Structural studies have shown that LNA oligonucleotides induce A-type (RNA-like) double-stranded conformations. Mechanistically, the 2'-O and 4'-C atoms on the ribose of LNA form a methylene bridge through different condensation interactions and are connected into a ring, thus "locking" the ribose ring in the desired Watson-Crick binding conformation. When incorporated into DNA or RNA Oligos, LNA can pair with complementary nucleotide strands faster and improve the stability of the resulting duplex. LNA has high thermal stability and is an ideal modification method for gene function (mRNA, non-coding RNA), inhibitory reagents ASO, inhibitor, antagomir and other RNA. Moreover, it can also be used in various probes and PCR primers, and suitable for detecting highly similar but short-length sequences, DNA, or long RNA sequences (such as mRNA). LNA-modified antisense nucleotides have become a new generation of antisense nucleic acid drugs.
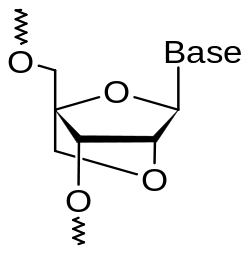 Fig.1 Chemical structure of an LNA monomer: additional bridge bond between the 2' oxygen and the 4' carbon of the pentose
Fig.1 Chemical structure of an LNA monomer: additional bridge bond between the 2' oxygen and the 4' carbon of the pentose
BOC Sciences can provide oligonucleotide synthesis services according to customers' design sequence or LNA modification requirements, such as modification sites, quantity, phosphorylation requirements, etc.

LNA modifications significantly increase thermal stability and binding affinity, allowing for shorter oligonucleotide sequences with enhanced specificity and improved nuclease resistance.
Each LNA monomer typically increases Tm by 2-8°C, enabling the design of shorter, more specific probes while maintaining optimal hybridization temperatures.
Key applications include FISH probes for in situ hybridization, real-time PCR probes, SNP detection assays, microarray analysis, and antisense research requiring high specificity.
Strategic placement considers sequence context, with modifications typically positioned at ends or around critical bases to maximize specificity while minimizing self-complementarity.
All LNA oligonucleotides undergo comprehensive QC including HPLC purification, mass spectrometry verification, and functional validation to ensure batch-to-batch consistency.
Yes, LNA can be effectively combined with various modifications including fluorescent dyes, biotin labels, and phosphorothioate backbones for multifunctional applications.
References