As a leading biotechnology company, BOC Sciences provides bridging nucleic acid (BNA) oligonucleotide synthesis services to customers worldwide with its proprietary nucleic acid technology. The third-generation nucleic acid analog, BNA, has better affinity and stability, and can better meet the specific needs of customers.
| Service | Custom BNA Oligonucleotide Synthesis | |
| Scales |
| |
| Modification |
| |
| Purification | Desalted, deprotected, PAGE, HPLC, and/or MS | |
| Quality Control | All custom BNA are manufactured under strict SOP quality control processes and checked for their quality | |
| Price | Inquiry | |
Bridging nucleic acid (BNA) is a novel nucleic acid analogue. The first generation BNA, LNA, is a bicyclic nucleotide analogue. LNA has good RNA-specific binding affinity. The second generation BNA, BNANC (2'-O,4'-amino ethylene bridging nucleic acid) is a six-membered bridging oligonucleotide. Oligonucleotides containing BNANC are more thermostable and water-soluble and lead to RNase H degradation of the target RNA. The new generation of BNA contains a five-membered or six-membered bridged structure with a fixed" C3'-endo sugar puckering. This bridge binds to the 2', 4' position of the ribose to obtain a 2', 4'-BNA monomer. The potential of the new generation BNA is the iteration of various BNAs. Such as, the recent synthesis of (S)-cEt-BNA, amino-BNA (AmNA), sulphonamide-BNA, guanidino-BNA and benzylidene acetal-type BNA. Compared with the previous generations of restricted nucleic acids (LNA or BNANC), the new generation of BNA exhibits a remarkably high affinity for its complementary strand. Their extraordinary levels of sensitivity and specificity for nucleic acid resistance make BNAs an excellent tool for the development of high-value detection systems and therapeutic products.
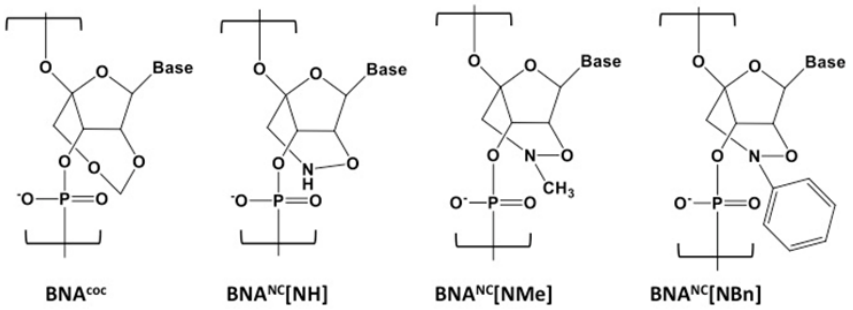 Fig. 1 The structure of BNAcoc and other 2', 4' BNANC nucleic acids. (Kim S, 2015)
Fig. 1 The structure of BNAcoc and other 2', 4' BNANC nucleic acids. (Kim S, 2015)
Incorporation of BNA into oligonucleotides allows the production of modified synthetic oligonucleotides with the following characteristics:
BNA incorporates advanced bridged structures with optimized ring sizes that provide superior binding affinity, enhanced nuclease resistance, and improved specificity compared to first-generation LNA technology.
BNA modifications significantly increase thermal stability, enhance hybridization specificity, and improve resistance to enzymatic degradation, making them ideal for demanding applications requiring high precision.
Multiple BNA variants including 2',4'-BNA, BNANC, and novel bridged structures are available, each offering distinct advantages in affinity, specificity, and biochemical properties.
Yes, BNA can be effectively integrated with various backbone modifications, fluorescent labels, and functional groups to create multifunctional oligonucleotides for complex research applications.


References